Particle Force
General
Inside the flag "force" a seperate power source can be adjusted for every single emitter. To activate this power source, please choose the strength unequal to 0, for deactivation set the strength exactly to 0.
Force source (type of power)
During the endurance of the particles, the force affects more or less all particles and pushes them to a special direction. An example for a force could be gravitation.
- Directional - Everywhere in the area the force similarily affects all direction. It has no position, but comes from endlessly far away and is equal strong at every position. (sunlight would be a good comparison).
- Directional from point - The force affects everywhere in the area the same direction, but its strength decreases with incremental distance of the particle from the position of the force.
- Point
The force moves from a special point in the area and pushes the particles away from this point (positive strength) or pulls it there (negative strength). The strength of the force decreases with incremental distance of the particle from the position of the force.
Strength of the force
The force affects the particles with the adjusted strength. If the values are negative, the force affects against the adjusted direction respectively concerning the "point force" acts inwardly instead of outwards.
| Attention! If the strength is 1.0-2.0 it starts to be intense. If the particles are flying rapidly it makes sense to reduce the endurance, so that the particles do not fly too long outside of the viewable area (which takes too much calculating power). |
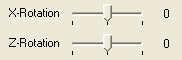
Direction of the force
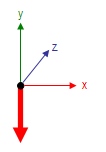
Figure: Force with X- and Z-turning to 0°
The direction of the force is adjusted analog to the direction of the emitter. But there is one exception: The values of the angles assume from a force directed downwards (negative Y-direction).
Position of the force
Origin of the force. If the type of force is Directional from point the force decreases with incremental distance of the particle from the position of the force. If it is point the force acts furthermore from the direction of the point and is capable to push or pull particles. Choose the adjustment like you see above: X- and Y- axis in the screen layer, the Z-axis points into the screen.